Recipes & examples
Enable trace logging of HTTP requests/responses
If you want to debug one of your monitors, you can enable trace logging of HTTP requests and responses. This will log all the requests and responses made by Kuvasz to your monitors. All you need to do is to add the following configuration to your YAML configuration file:
- You can also use
DEBUG, but it won't log the request and response bodies, only the headers and status codes.
Home Assistant RESTful integration
Kuvasz can be easily integrated with Home Assistant using the RESTful integration by using its API. This allows you to create sensors for your most precious monitors and use them in your automations, scripts, or just to visualize the status of your monitors. You can even build your own custom dashboard with the data from your monitors!
Tip
If you have the authentication disabled, you can skip setting up your API key as a secret and you can also omit the X-API-KEY header in your requests.
Define your secret in Home Assistant
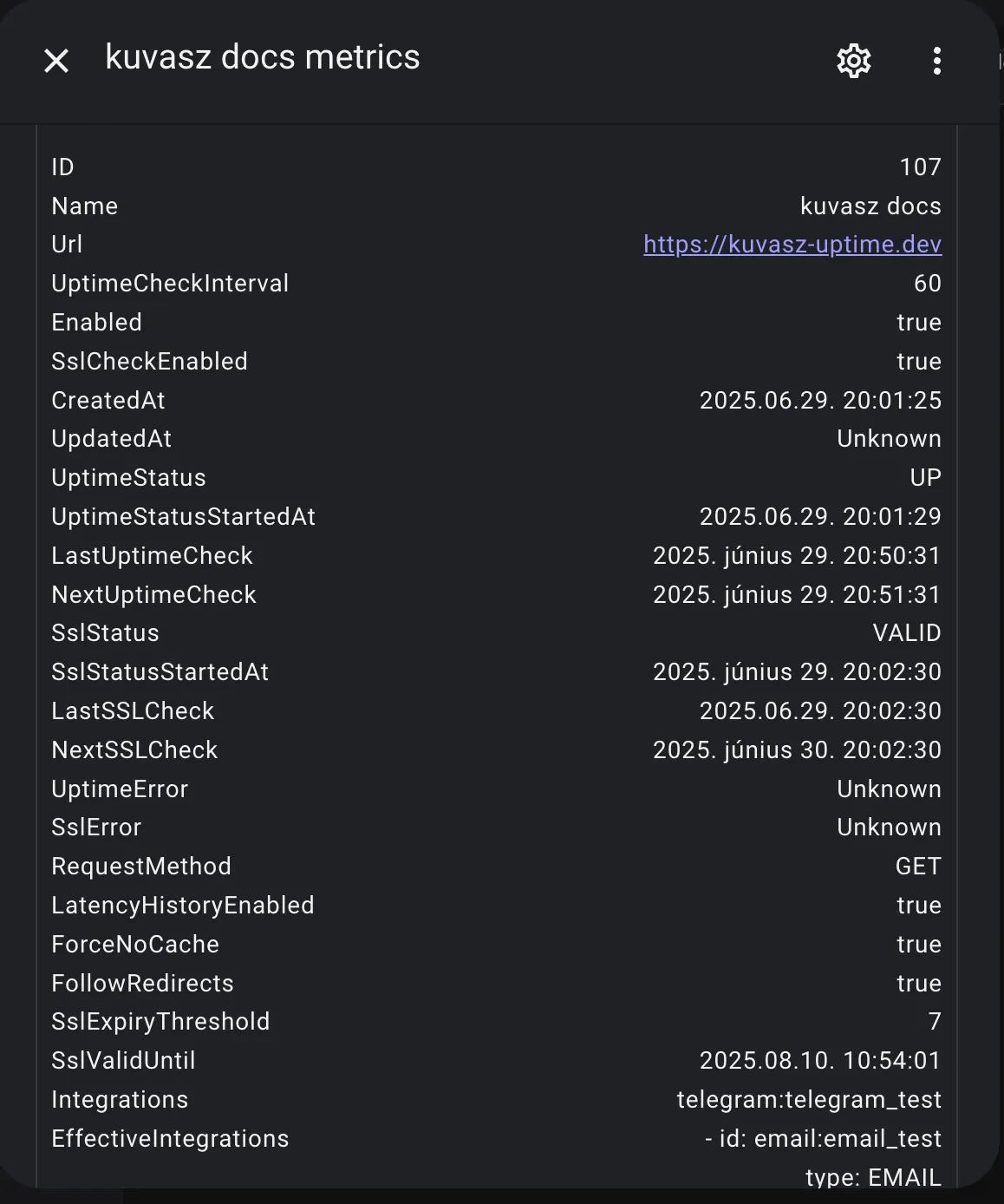
Sensor with JSON attributes
sensor:
- name: "kuvasz docs metrics"
unique_id: metrics_kuvasz_docs
platform: rest
verify_ssl: false
scan_interval: 60
resource: http://kuvasz.home/api/v2/http-monitors/107
headers:
X-API-KEY: !secret kuvasz_api_key
value_template: "OK"
json_attributes:
- id
- name
- url
- uptimeCheckInterval
- enabled
- sslCheckEnabled
- createdAt
- updatedAt
- uptimeStatus
- uptimeStatusStartedAt
- lastUptimeCheck
- nextUptimeCheck
- sslStatus
- sslStatusStartedAt
- lastSSLCheck
- nextSSLCheck
- uptimeError
- sslError
- requestMethod
- latencyHistoryEnabled
- forceNoCache
- followRedirects
- sslExpiryThreshold
- failureCountThreshold
- sslValidUntil
- integrations
- effectiveIntegrations
Result:
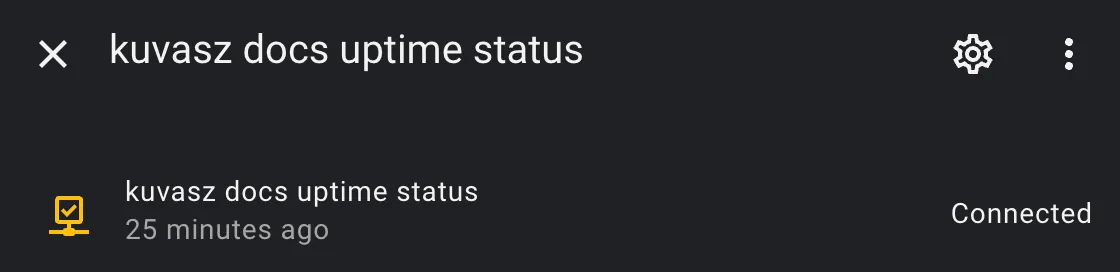
Binary sensor for uptime as connectivity
binary_sensor:
- name: "kuvasz docs uptime status"
unique_id: uptime_kuvasz_docs
platform: rest
verify_ssl: false
scan_interval: 60
resource: http://kuvasz.home/api/v2/http-monitors/107
headers:
X-API-KEY: !secret kuvasz_api_key
device_class: connectivity
value_template: >
{% set status = value_json.uptimeStatus %}
{{ status == 'UP' }}
availability: >
{{ value_json.uptimeStatus is not none }}
Result:
Exposing status pages on subdomains behind a reverse proxy
If you want to expose your status pages on subdomains (e.g. status.yourdomain.com), you can do so by using a reverse proxy (e.g. Caddy, Nginx, Traefik, etc.). Here is an example configuration for Caddy:
status.your-domain.com {
reverse_proxy {YOUR_KUVASZ_HOST}:8080
rewrite /public/* {uri} # (1)!
rewrite * /status{uri} # (2)!
}
- This is needed to serve the static assets (CSS, JS, images, etc.) correctly.
- This will rewrite all requests to
/status, which is the path where the status pages are served.
The configuration snippet above exposes the default status page (that is located under /status on Kuvasz) on the root of the configured subdomain (i.e. status.your-domain.com), and also proxies the other status pages (e.g. /status/your-custom-status-page) on requesting status.your-domain.com/your-custom-status-page.
Providing a custom root certificate for SSL checks
If you want to use a custom root certificate for SSL checks (e.g. if you're using a self-signed certificate, or a private CA), you can provide it by modifying the Java Keystore (JKS) in use, to add your custom root certificate to it.
The advantage of this approach is, that you only need to do the following steps when:
- you have a new cert, or you would like to update the existing custom one
- we change the base image of the Docker build (should not happen in the near future)
- we change the Java version in the project (happens really not that often)
Otherwise you can just use your own "patched" cacerts for every new version of Kuvasz.
Preparing the custom cacerts file
# 1. Pull the current base image
docker pull eclipse-temurin:25-jre-alpine-3.23
# 2. Copy the "original" cacerts to a local file
docker run --rm --entrypoint cat eclipse-temurin:25-jre-alpine-3.23 /opt/java/openjdk/lib/security/cacerts > cacerts
# 3. This is the tricky step: we attach back the current folder where the cacerts, and also the custom certificate should exist and we add the custom certificate to the keystore
docker run --rm -v `pwd`:/tmp/certs eclipse-temurin:25-jre-alpine-3.23 sh -c 'cd /tmp/certs && keytool -keystore cacerts -storepass changeit -noprompt -trustcacerts -importcert -alias your-custom-alias -file your-custom-cert.crt'
Watch out for your-custom-alias and your-custom-cert.crt in the example, these are the moving parts, depending on your own preferences.
Attaching the modified cacerts to Kuvasz
This is easier, and quite straightforward, you just need to mount another volume with your cacerts file from the steps above:
Backup & Restore with YAML
It might be useful to create sometimes a backup from your monitors and status pages in case you didn't configure them via a YAML file, because later you might want to switch to that method, or you just want to make it possible to restore them in case of an accidental deletion, for example.
- To do so, you can use the Web UI (Settings > Backup & Restore) or the API (Monitors, Status pages). The response in both cases will be a YAML file, which you can save to a safe place.
- To restore those files, you can just simply copy the content of them as-is into your own YAML configuration file, and restart your instance of Kuvasz.
- If you would like to continue using the UI or the API to manage your monitors and status pages, you need to remove the corresponding sections from your YAML configuration file after the successful restore and restart your instance once again. After that, you should be able to manage everything via the UI or the API as before.
Homepage integration
Homepage is a really nice open-source tool to create a personal dashboard with links, widgets, and more. You can integrate Kuvasz into your homepage dashboard by using their custom API widget.
The examples below doesn't necessarily map all the possible fields, but it gives you a good starting point to create your own widgets.
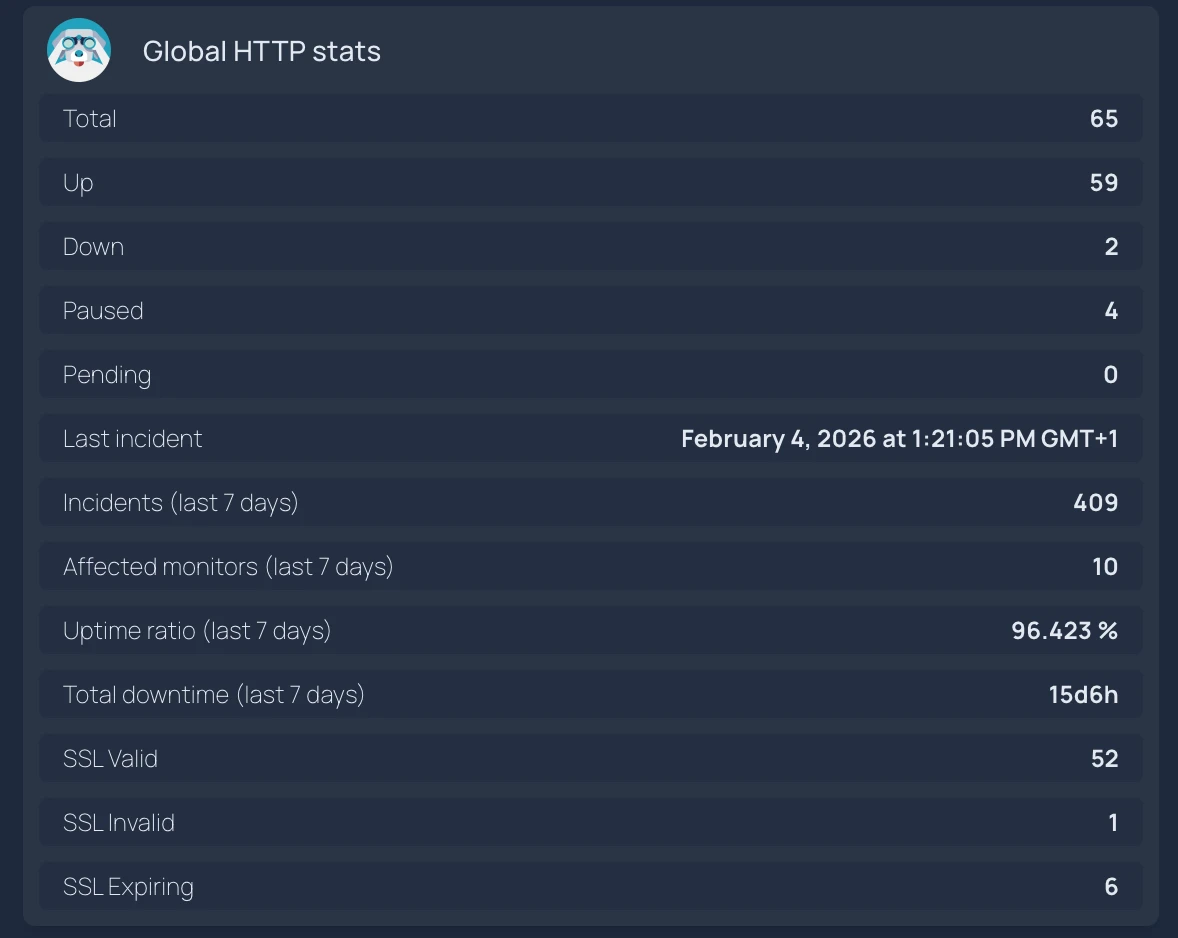
Global HTTP stats
- Global HTTP stats:
id: kuvasz-http-stats
icon: sh-kuvasz
widget:
type: customapi
display: list
url: https://demo.kuvasz-uptime.dev/api/v2/http-monitors/stats
refreshInterval: 300
headers:
X-Api-Key: KuvaszDemoAPIKey
mappings:
- label: Total
field: actual.uptimeStats.total
- label: Up
field: actual.uptimeStats.up
- label: Down
field: actual.uptimeStats.down
- label: Paused
field: actual.uptimeStats.paused
- label: Pending
field: actual.uptimeStats.inProgress
- label: Last incident
field: actual.uptimeStats.lastIncident
format: date
locale: en
dateStyle: long
timeStyle: long
- label: Incidents (last 7 days)
field: history.uptimeStats.incidents
- label: Affected monitors (last 7 days)
field: history.uptimeStats.affectedMonitors
- label: Uptime ratio (last 7 days)
field: history.uptimeStats.uptimeRatio
format: float
scale: 100
suffix: '%'
- label: Total downtime (last 7 days)
field: history.uptimeStats.totalDowntimeSeconds
format: duration
- label: SSL Valid
field: actual.sslStats.valid
- label: SSL Invalid
field: actual.sslStats.invalid
- label: SSL Expiring
field: actual.sslStats.willExpire
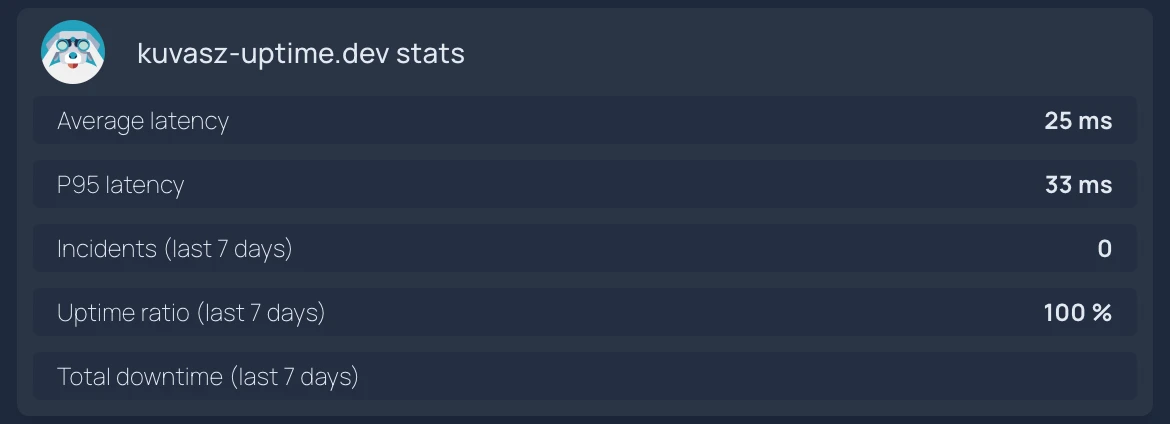
Individual monitor stats
- kuvasz-uptime.dev stats:
id: kuvasz-uptime-http-stats
icon: sh-kuvasz
widget:
type: customapi
display: list
url: https://demo.kuvasz-uptime.dev/api/v2/http-monitors/38/stats
refreshInterval: 300
headers:
X-Api-Key: KuvaszDemoAPIKey
mappings:
- label: Average latency
field: latencyStats.averageLatencyInMs
format: number
suffix: ms
- label: P95 latency
field: latencyStats.p95LatencyInMs
format: number
suffix: ms
- label: Incidents (last 7 days)
field: uptimeHistory.incidents
- label: Uptime ratio (last 7 days)
field: uptimeHistory.uptimeRatio
format: float
scale: 100
suffix: '%'
- label: Total downtime (last 7 days)
field: uptimeHistory.totalDowntimeSeconds
format: duration
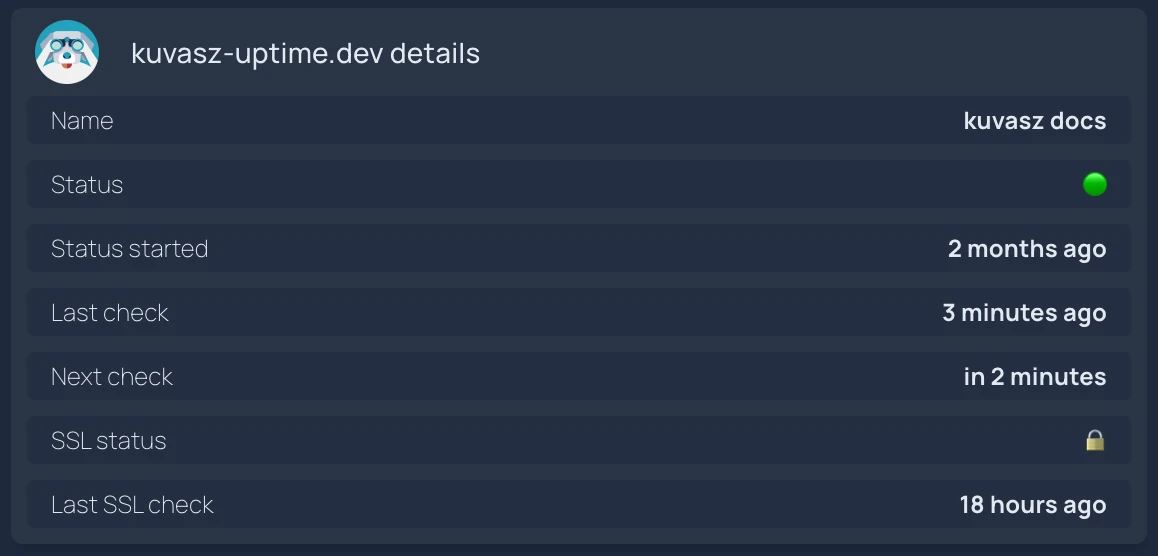
Individual monitor details
- kuvasz-uptime.dev details:
id: kuvasz-uptime-http-details
icon: sh-kuvasz
widget:
type: customapi
display: list
url: https://demo.kuvasz-uptime.dev/api/v2/http-monitors/38
refreshInterval: 300
headers:
X-Api-Key: KuvaszDemoAPIKey
mappings:
- label: Name
field: name
- label: Status
field: uptimeStatus
remap:
- value: UP
to: 🟢
- value: DOWN
to: 🔴
- any: true
to: 🟡
- label: Status started
field: uptimeStatusStartedAt
format: relativeDate
locale: en
style: long
- label: Last check
field: lastUptimeCheck
format: relativeDate
locale: en
style: long
- label: Next check
field: nextUptimeCheck
format: relativeDate
locale: en
style: long
- label: SSL status
field: sslStatus
remap:
- value: VALID
to: 🔒
- value: INVALID
to: 🔓
- value: WILL_EXPIRE
to: 🕣
- any: true
to: 🟡
- label: Last SSL check
field: lastSSLCheck
format: relativeDate
locale: en
style: long
Overview with a clickable list of monitors
- Monitors:
id: kuvasz-uptime-http-dynamic-list
icon: sh-kuvasz
widget:
type: customapi
display: dynamic-list
url: https://demo.kuvasz-uptime.dev/api/v2/http-monitors?enabled=true
refreshInterval: 300
headers:
X-Api-Key: KuvaszDemoAPIKey
mappings:
name: name
label: uptimeStatus
limit: 5
format: text
remap:
- value: UP
to: 🟢
- value: DOWN
to: 🔴
- any: true
to: 🟡
target: https://demo.kuvasz-uptime.dev/http-monitors/{id}
Full YAML example (app-config + monitors + integrations)
This is just a full example of a YAML configuration file, which you can use as a starting point for your own configuration. You can copy and paste it into your own configuration file, and then modify it to suit your needs, but always make sure that you read the corresponding documentation sections for each feature or integration you want to use.
Warning
Be aware that if you define your monitors or your status pages via YAML, you cannot use the Web UI to modify them, you can only view them there!
micronaut.security.enabled: true
micronaut.security.token.generator.access-token.expiration: 86400 # 24 hours
admin-auth:
username: YourSuperSecretUsername
password: YourSuperSecretPassword
api-key: ThisShouldBeVeryVerySecureToo
app-config:
event-data-retention-days: 365
latency-data-retention-days: 7
log-event-handler: true
language: en
check-updates: true
http-check-timeout-seconds: 30
---
smtp-config:
host: 'your.smtp.server'
port: 465
transport-strategy: SMTP_TLS
username: YourSMTPUsername
password: YourSMTPPassword
---
integrations:
pagerduty:
- name: pd_global
integration-key: YourOwnIntegrationKey
global: true
enabled: true
slack:
- name: slack_default
webhook-url: 'https://hooks.slack.com/services/T00000000/B00000000/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX'
discord:
- name: discord
webhook-url: https://discord.com/api/webhooks/XXXXXXX/YYYYYYYYY
email:
- name: email_implicitly_enabled
from-address: noreply@kuvasz-uptime.dev
to-address: your@email.address
telegram:
- name: telegram_disabled
api-token: 'YourToken'
chat-id: '-1232642423121'
enabled: false
---
http-monitors:
- name: "full configuration example"
url: "https://akobor.me"
uptime-check-interval: 30
enabled: true
ssl-check-enabled: false
request-method: "POST"
latency-history-enabled: true
follow-redirects: true
force-no-cache: true
ssl-expiry-threshold: 30
failure-count-threshold: 2
integrations:
- "telegram:telegram_disabled"
- "slack:slack_default"
expected-status-codes:
- 200
- 201
- 303
expected-keyword: "akobor"
expected-keyword-case-sensitive: true
expected-keyword-negated: false
response-time-threshold-millis: 500
request-headers:
Host: "example.com"
expected-headers:
Content-Type: "application/json"
request-body: "{\"key\":\"value\"}"
- name: "minimal configuration example"
url: "https://kuvasz-uptime.dev"
uptime-check-interval: 5
push-monitors:
- name: "My Push Monitor"
heartbeat-interval: 10
grace-period: 2
failure-count-threshold: 3
client-secret: "d6d5a85c-82c0-4bea-9926-c3eed32de32b"
enabled: true
integrations: [ ]
- name: "Another Push Monitor"
heartbeat-interval: 86400
grace-period: 3600
client-secret: "7b2d5cb1-41bd-4067-9732-c79dbbf45286"
enabled: false
integrations:
- "slack:slack_default"
---
default-status-page:
public: true
title: "Status - Kuvasz Uptime"
custom-logo-url: "https://example.com/logo.png"
custom-favicon-url: "https://example.com/favicon.png"
status-pages:
- title: "Example Status Page"
slug: "example-status"
public: true
custom-logo-url: "https://example.com/logo.png"
custom-favicon-url: "https://example.com/favicon.png"
monitors:
- "http:full configuration example"
- "http:minimal configuration example"
- "push:My Push Monitor"